The one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) in Python
Zhijun / 2021-12-10
The date from Vc contents of different fruits were used to perform ANOVA.
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df.head(n=20)## Number Fruit Repeat Vitamin
## 0 1 Apple A1 4.6
## 1 2 Apple A2 3.9
## 2 3 Apple A3 5.2
## 3 4 Apple A4 6.9
## 4 5 Apple A5 4.8
## 5 6 Apple A6 3.3
## 6 7 Banana A1 8.7
## 7 8 Banana A2 8.8
## 8 9 Banana A3 10.3
## 9 10 Banana A4 11.5
## 10 11 Banana A5 12.7
## 11 12 Banana A6 9.6
## 12 13 Watermelon A1 8.1
## 13 14 Watermelon A2 8.5
## 14 15 Watermelon A3 7.5
## 15 16 Watermelon A4 8.4
## 16 17 Watermelon A5 10.3
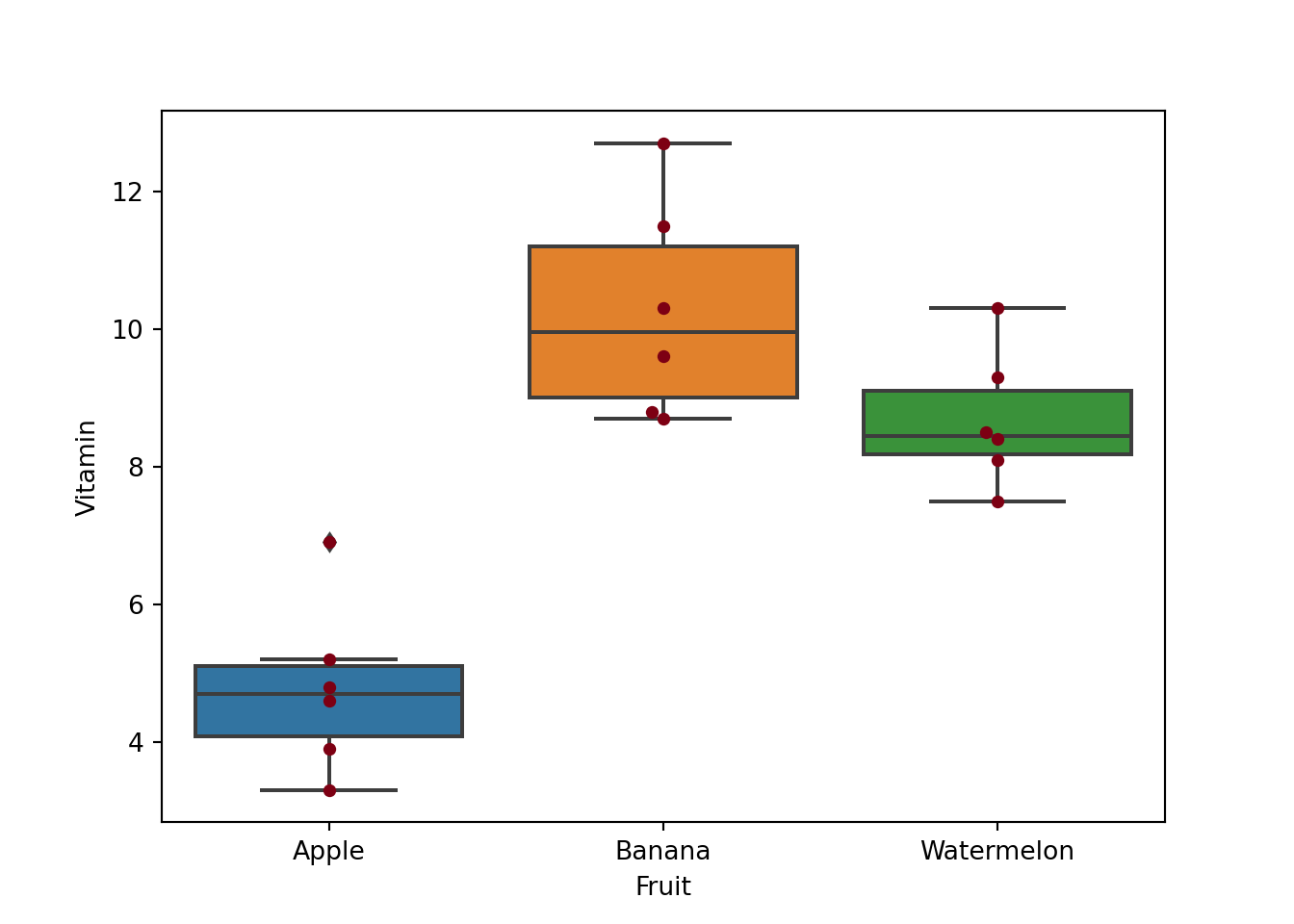
## 17 18 Watermelon A6 9.3To generate a box plot to see the data distribution by treatments.
plt_2 = sns.boxplot(x="Fruit", y="Vitamin",data = df)
plt_3 = sns.swarmplot(x="Fruit", y="Vitamin",data = df, color='#7d0013')
plt.show()To show the results of mean SD values:
import scipy.stats as stats
# reshape the d dataframe suitable for statsmodels package
df_wide=pd.pivot(data = df, index='Repeat', columns = 'Fruit', values = 'Vitamin') #Reshape from long to wide
# stats f_oneway functions takes the groups as input and returns ANOVA F and p value
df_wide.head()## Fruit Apple Banana Watermelon
## Repeat
## A1 4.6 8.7 8.1
## A2 3.9 8.8 8.5
## A3 5.2 10.3 7.5
## A4 6.9 11.5 8.4
## A5 4.8 12.7 10.3fvalue, pvalue = stats.f_oneway(df_wide['Apple'], df_wide['Banana'], df_wide['Watermelon'])
print(fvalue, pvalue)## 28.658869785419157 7.5222561940802785e-06The results indicated that the p value is less than 0.05, which means that the difference between the means of the groups is statistically significant.
# get ANOVA table as R like output
import statsmodels.api as sm
from statsmodels.formula.api import ols
# Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) model
model = ols('Vitamin ~ C(Fruit)', data=df).fit()
anova_table = sm.stats.anova_lm(model, typ=2)
anova_table
# ANOVA table using bioinfokit v1.0.3 or later (it uses wrapper script for anova_lm)## sum_sq df F PR(>F)
## C(Fruit) 95.567778 2.0 28.65887 0.000008
## Residual 25.010000 15.0 NaN NaNfrom bioinfokit.analys import stat
res = stat()
res.anova_stat(df=df, res_var='Vitamin', anova_model='Vitamin ~ C(Fruit)')
res.anova_summary## df sum_sq mean_sq F PR(>F)
## C(Fruit) 2.0 95.567778 47.783889 28.65887 0.000008
## Residual 15.0 25.010000 1.667333 NaN NaNShapiro-Wilk test can be used to check the normal distribution of residuals
import scipy.stats as stats
w, pvalue = stats.shapiro(model.resid)
print(w, pvalue)## 0.9351375699043274 0.2388565093278885As the p value is non significant, we fail to reject null hypothesis and conclude that data is drawn from normal distribution.
perform multiple pairwise comparison (Tukey’s HSD)
# unequal sample size data, tukey_hsd uses Tukey-Kramer test
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
res = stat()
res.tukey_hsd(df=df, res_var='Vitamin', xfac_var='Fruit', anova_model='Vitamin~ C(Fruit)')
res.tukey_summary## group1 group2 Diff Lower Upper q-value p-value
## 0 Apple Banana 5.483333 3.547664 7.419003 10.401813 0.001000
## 1 Apple Watermelon 3.900000 1.964331 5.835669 7.398250 0.001000
## 2 Banana Watermelon 1.583333 -0.352336 3.519003 3.003563 0.118396